Outer space
Outer Space by Rishabh Sharma on Scribd
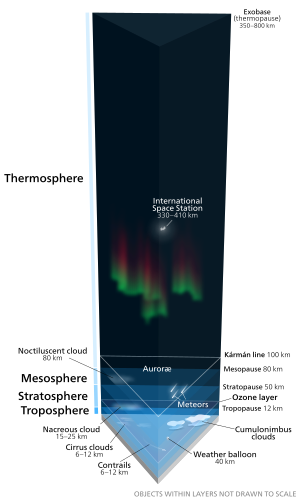 |
The interface between the Earth's surface and outer space. The Kármán line at a height of 100 km (62 mi) is shown. The layers of the atmosphere are drawn to scale, whereas objects within them, such as the International Space Station, are not. |
There is no firm boundary where outer space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.
Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.
Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.
Discovery
In 350 BCE, Greek philosopher Aristotle suggested that nature abhors a vacuum, a principle that became known as the horror vacui. This concept built upon a 5th-century BCE ontological argument by the Greek philosopher Parmenides, who denied the possible existence of a void in space. Based on this idea that a vacuum could not exist, in the West it was widely held for many centuries that space could not be empty. As late as the 17th century, the French philosopher René Descartes argued that the entirety of space must be filled.In ancient China, there were various schools of thought concerning the nature of the heavens, some of which bear a resemblance to the modern understanding. In the 2nd century, astronomer Zhang Heng became convinced that space must be infinite, extending well beyond the mechanism that supported the Sun and the stars. The surviving books of the Hsüan Yeh school said that the heavens were boundless, "empty and void of substance". Likewise, the "sun, moon, and the company of stars float in the empty space, moving or standing still".
The Italian scientist Galileo Galilei knew that air had mass and so was subject to gravity. In 1640, he demonstrated that an established force resisted the formation of a vacuum. However, it would remain for his pupil Evangelista Torricelli to create an apparatus that would produce a vacuum in 1643. This experiment resulted in the first mercury barometer and created a scientific sensation in Europe. The French mathematician Blaise Pascal reasoned that if the column of mercury was supported by air then the column ought to be shorter at higher altitude where the air pressure is lower. In 1648, his brother-in-law, Florin Périer, repeated the experiment on the Puy de Dôme mountain in central France and found that the column was shorter by three inches. This decrease in pressure was further demonstrated by carrying a half-full balloon up a mountain and watching it gradually expand, then contract upon descent.
 |
The original Magdeburg hemispheres (lower left) used to demonstrate Otto von Guericke's vacuum pump (right) |
Back in the 15th century, German theologian Nicolaus Cusanus speculated that the Universe lacked a center and a circumference. He believed that the Universe, while not infinite, could not be held as finite as it lacked any bounds within which it could be contained. These ideas led to speculations as to the infinite dimension of space by the Italian philosopher Giordano Bruno in the 16th century. He extended the Copernican heliocentric cosmology to the concept of an infinite Universe filled with a substance he called aether, which did not cause resistance to the motions of heavenly bodies. English philosopher William Gilbert arrived at a similar conclusion, arguing that the stars are visible to us only because they are surrounded by a thin aether or a void. This concept of an aether originated with ancient Greek philosophers, including Aristotle, who conceived of it as the medium through which the heavenly bodies moved.
The concept of a Universe filled with a luminiferous aether remained in vogue among some scientists until the early 20th century. This form of aether was viewed as the medium through which light could propagate. In 1887, the Michelson–Morley experiment tried to detect the Earth's motion through this medium by looking for changes in the speed of light depending on the direction of the planet's motion. However, the null result indicated something was wrong with the concept. The idea of the luminiferous aether was then abandoned. It was replaced by Albert Einstein's theory of special relativity, which holds that the speed of light in a vacuum is a fixed constant, independent of the observer's motion or frame of reference.
The first professional astronomer to support the concept of an infinite Universe was the Englishman Thomas Digges in 1576. But the scale of the Universe remained unknown until the first successful measurement of the distance to a nearby star in 1838 by the German astronomer Friedrich Bessel. He showed that the star 61 Cygni had a parallax of just 0.31 arcseconds (compared to the modern value of 0.287″). This corresponds to a distance of over 10 light years. The distance to the Andromeda Galaxy was determined in 1923 by American astronomer Edwin Hubble by measuring the brightness of cepheid variables in that galaxy, a new technique discovered by Henrietta Leavitt. This established that the Andromeda galaxy, and by extension all galaxies, lay well outside the Milky Way.
The earliest known estimate of the temperature of outer space was by the Swiss physicist Charles É. Guillaume in 1896. Using the estimated radiation of the background stars, he concluded that space must be heated to a temperature of 5–6 K. British physicist Arthur Eddington made a similar calculation to derive a temperature of 3.18 K in 1926. 1933 German physicist Erich Regener used the total measured energy of cosmic rays to estimate an intergalactic temperature of 2.8 K.
The modern concept of outer space is based on the "Big Bang" cosmology, first proposed in 1931 by the Belgian physicist Georges Lemaître. This theory holds that the observable universe originated from a very compact form that has since undergone continuous expansion. The background energy released during the initial expansion has steadily decreased in density, leading to a 1948 prediction by American physicts Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman of a temperature of 5 K for the temperature of space.
The term outer space was used in 1842 by the English poet Lady Emmeline Stuart-Wortley in her poem "The Maiden of Moscow". The expression outer space was used as an astronomical term by Alexander von Humboldt in 1845. It was later popularized in the writings of H. G. Wells in 1901. The shorter term space is actually older, first used to mean the region beyond Earth's sky in John Milton's Paradise Lost in 1667.
Formation and state
 |
This is an artist's concept of the metric expansion of space, where a volume of the Universe is represented at each time interval by the circular sections. At left is depicted the rapid inflation from the initial state, followed thereafter by steady expansion to the present day, shown at right. |
The present day shape of the Universe has been determined from measurements of the cosmic microwave background using satellites like the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe. These observations indicate that the observable universe is "flat", meaning that photons on parallel paths at one point will remain parallel as they travel through space to the limit of the observable universe, except for local gravity. The flat Universe, combined with the measured mass density of the Universe and the accelerating expansion of the Universe, indicates that space has a non-zero vacuum energy, which is called dark energy.
Estimates put the average energy density of the Universe at the equivalent of 5.9 protons per cubic meter, including dark energy, dark matter, and baryonic matter (ordinary matter composed of atoms). The atoms account for only 4.6% of the total energy density, or a density of one proton per four cubic meters. The density of the Universe, however, is clearly not uniform; it ranges from relatively high density in galaxies—including very high density in structures within galaxies, such as planets, stars, and black holes—to conditions in vast voids that have much lower density, at least in terms of visible matter. Unlike the matter and dark matter, the dark energy seems not to be concentrated in galaxies: although dark energy may account for a majority of the mass-energy in the Universe, dark energy's influence is 5 orders of magnitude smaller than the influence of gravity from matter and dark matter within the Milky Way.
Environment
 |
Part of the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field image showing a typical section of space containing galaxies interspersed by deep vacuum. Given the finite speed of light, this view covers the last 13 billion years of the history of outer space. |
Stars, planets and moons retain their atmospheres by gravitational attraction. Atmospheres have no clearly delineated boundary: the density of atmospheric gas gradually decreases with distance from the object until it becomes indistinguishable from the surrounding environment. The Earth's atmospheric pressure drops to about 0.032 Pa at 100 kilometres (62 miles) of altitude, compared to 100,000 Pa for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) definition of standard pressure. Beyond this altitude, isotropic gas pressure rapidly becomes insignificant when compared to radiation pressure from the Sun and the dynamic pressure of the solar wind. The thermosphere in this range has large gradients of pressure, temperature and composition, and varies greatly due to space weather.
The temperature of the vacuum is measured in terms of the kinetic activity of the gas, as it is on Earth. However, the radiation that fills the vacuum has a different temperature than the kinetic temperature of the gas, meaning that the gas and radiation are not in thermodynamic equilibrium. All of the observable universe is filled with photons that were created during the Big Bang, which is known as the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). (There is quite likely a correspondingly large number of neutrinos called the cosmic neutrino background.) The current black body temperature of the background radiation is about 3 K (−270 °C; −454 °F). The gas temperatures in outer space are always at least the temperature of the CMB but can be much higher. For example, the corona of the Sun has temperatures which range over 1.2–2.6 million K.
Outside a protective atmosphere and magnetic field, there are few obstacles to the passage through space of energetic subatomic particles known as cosmic rays. These particles have energies ranging from about 106 eV up to an extreme 1020 eV of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. The peak flux of cosmic rays occurs at energies of about 109 eV, with approximately 87% protons, 12% helium nuclei and 1% heavier nuclei. In the high energy range, the flux of electrons is only about 1% of that of protons. Cosmic rays can damage electronic components and pose a health threat to space travelers. According to astronauts, like Don Pettit, space has a burned/metallic odor that clings to their suits and equipment, similar to the scent of an arc welding torch.
Despite the harsh environment, several life forms have been found that can withstand extreme space conditions for extended periods. Species of lichen carried on the ESA BIOPAN facility survived exposure for ten days in 2007. Seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana tabacum germinated after being exposed to space for 1.5 years. A strain of bacillus subtilis has survived 559 days when exposed to low-Earth orbit or a simulated martian environment. The lithopanspermia hypothesis suggests that rocks ejected into outer space from life-harboring planets may successfully transport life forms to another habitable world. A conjecture is that just such a scenario occurred early in the history of the Solar System, with potentially microorganism-bearing rocks being exchanged between Venus, Earth, and Mars.
Effect on human bodies
 |
Because of the hazards of a vacuum, astronauts must wear a pressurized space suit while off-Earth and outside their spacecraft. |
As a consequence of rapid decompression, any oxygen dissolved in the blood will empty into the lungs to try to equalize the partial pressure gradient. Once the deoxygenated blood arrives at the brain, humans and animals will lose consciousness after a few seconds and die of hypoxia within minutes. Blood and other body fluids boil when the pressure drops below 6.3 kPa, and this condition is called ebullism. The steam may bloat the body to twice its normal size and slow circulation, but tissues are elastic and porous enough to prevent rupture. Ebullism is slowed by the pressure containment of blood vessels, so some blood remains liquid. Swelling and ebullism can be reduced by containment in a flight suit. The Crew Altitude Protection Suit (CAPS), a fitted elastic garment designed in the 1960s for Shuttle astronauts, prevents ebullism at pressures as low as 2 kPa. Space suits are needed at 8 km (5.0 mi) to provide enough oxygen for breathing and to prevent water loss, while above 20 km (12 mi) they are essential to prevent ebullism. Most space suits use around 30–39 kPa of pure oxygen, about the same as on the Earth's surface. This pressure is high enough to prevent ebullism, but evaporation of nitrogen dissolved in the blood could still cause decompression sickness and gas embolisms if not managed.
Humans evolved for life in Earth gravity, and exposure to weightlessness has been shown to have deleterious effects on the health of the human body. Initially, more than 50% of astronauts experience space motion sickness. This can cause nausea and vomiting, vertigo, headaches, lethargy, and overall malaise. The duration of space sickness varies, but it typically lasts for 1–3 days, after which the body adjusts to the new environment. Longer term exposure to weightlessness results in muscle atrophy and deterioration of the skeleton, or spaceflight osteopenia. These effects can be minimized through a regimen of exercise. Other effects include fluid redistribution, slowing of the cardiovascular system, decreased production of red blood cells, balance disorders, and a weakening of the immune system. Lesser symptoms include loss of body mass, nasal congestion, sleep disturbance, and puffiness of the face.
For long duration space travel, radiation can pose an acute health hazard. Exposure to radiation sources such as high-energy, ionizing cosmic rays can result in fatigue, nausea, vomiting, as well as damage to the immune system and changes to the white blood cell count. Over longer durations, symptoms include an increased risk of cancer, plus damage to the eyes, nervous system, lungs and the gastrointestinal tract. On a round-trip Mars mission lasting three years, nearly the entire body would be traversed by high energy nuclei, each of which can cause ionization damage to cells. Fortunately, most such particles are significantly attenuated by the shielding provided by the aluminium walls of a spacecraft, and can be further diminished by water containers and other barriers. However, the impact of the cosmic rays upon the shielding produces additional radiation that can affect the crew. Further research will be needed to assess the radiation hazards and determine suitable countermeasures.
Boundary
 |
SpaceShipOne completed the first manned private spaceflight in 2004, reaching an altitude of 100.12 km (62.21 mi). |
- The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale has established the Kármán line at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) as a working definition for the boundary between aeronautics and astronautics. This is used because at an altitude of about 100 km (62 mi), as Theodore von Kármán calculated, a vehicle would have to travel faster than orbital velocity in order to derive sufficient aerodynamic lift from the atmosphere to support itself.
- The United States designates people who travel above an altitude of 50 miles (80 km) as astronauts.
- NASA's Space Shuttle used 400,000 feet (76 mi, 122 km) as its re-entry altitude (termed the Entry Interface), which roughly marks the boundary where atmospheric drag becomes noticeable, thus beginning the process of switching from steering with thrusters to maneuvering with air surfaces.
The altitude where the atmospheric pressure matches the vapor pressure of water at the temperature of the human body is called the Armstrong line, named after American physician Harry G. Armstrong. It is located at an altitude of around 19.14 km (11.89 mi). At or above the Armstrong line, fluids in the throat and lungs will boil away. More specifically, exposed bodily liquids such as saliva, tears, and the liquids wetting the alveoli within the lungs will boil away. Hence, at this altitude the human body requires a pressure suit, or a pressurized capsule, to survive.
Legal status
 |
2008 launch of the SM-3 missile used to destroy American spy satellite USA-193 |
Beginning in 1958, outer space has been the subject of multiple resolutions by the United Nations General Assembly. Of these, more than 50 have been concerning the international co-operation in the peaceful uses of outer space and preventing an arms race in space. Four additional space law treaties have been negotiated and drafted by the UN's Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space. Still, there remains no legal prohibition against deploying conventional weapons in space, and anti-satellite weapons have been successfully tested by the US, USSR and China. The 1979 Moon Treaty turned the jurisdiction of all heavenly bodies (including the orbits around such bodies) over to the international community. However, this treaty has not been ratified by any nation that currently practices manned spaceflight.
In 1976, eight equatorial states (Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Congo, Zaire, Uganda, Kenya, and Indonesia) met in Bogotá, Colombia. They made the "Declaration of the First Meeting of Equatorial Countries," also known as "the Bogotá Declaration", where they made a claim to control the segment of the geosynchronous orbital path corresponding to each country. These claims are not internationally accepted.
Earth orbit
A spacecraft enters orbit when it has enough horizontal velocity for its centripetal acceleration due to gravity to be less than or equal to the centrifugal acceleration due to the horizontal component of its velocity. For a low Earth orbit, this velocity is about 7,800 m/s (28,100 km/h; 17,400 mph); by contrast, the fastest manned airplane speed ever achieved (excluding speeds achieved by deorbiting spacecraft) was 2,200 m/s (7,900 km/h; 4,900 mph) in 1967 by the North American X-15.To achieve an orbit, a spacecraft must travel faster than a sub-orbital spaceflight. The energy required to reach Earth orbital velocity at an altitude of 600 km (370 mi) is about 36 MJ/kg, which is six times the energy needed merely to climb to the corresponding altitude. Spacecraft with a perigee below about 2,000 km (1,200 mi) are subject to drag from the Earth's atmosphere, which will cause the orbital altitude to decrease. The rate of orbital decay depends on the satellite's cross-sectional area and mass, as well as variations in the air density of the upper atmosphere. Below about 300 km (190 mi), decay becomes more rapid with lifetimes measured in days. Once a satellite descends to 180 km (110 mi), it will start to burn up in the atmosphere. The escape velocity required to pull free of Earth's gravitational field altogether and move into interplanetary space is about 11,200 m/s (40,300 km/h; 25,100 mph).
Earth's gravity reaches out far past the Van Allen radiation belt and keeps the Moon in orbit at an average distance of 384,403 km (238,857 mi). The region of space where the gravity of a planet tends to dominate the motion of objects in the presence of other perturbing bodies (such as another planet) is known as the Hill sphere. For Earth, this sphere has a radius of about 1,500,000 km (930,000 mi).
Regions
Space is a partial vacuum: its different regions are defined by the various atmospheres and "winds" that dominate within them, and extend to the point at which those winds give way to those beyond. Geospace extends from Earth's atmosphere to the outer reaches of Earth's magnetic field, whereupon it gives way to the solar wind of interplanetary space. Interplanetary space extends to the heliopause, whereupon the solar wind gives way to the winds of the interstellar medium. Interstellar space then continues to the edges of the galaxy, where it fades into the intergalactic void.Geospace
 |
Aurora australis observed from the Space Shuttle Discovery, on STS-39, May 1991 (orbital altitude: 260 km) |
The volume of geospace defined by the magnetopause is compacted in the direction of the Sun by the pressure of the solar wind, giving it a typical subsolar distance of 10 Earth radii from the center of the planet. However, the tail can extend outward to more than 100–200 Earth radii. The Moon passes through the geospace tail during roughly four days each month, during which time the surface is shielded from the solar wind.
Geospace is populated by electrically charged particles at very low densities, the motions of which are controlled by the Earth's magnetic field. These plasmas form a medium from which storm-like disturbances powered by the solar wind can drive electrical currents into the Earth’s upper atmosphere. During geomagnetic storms two regions of geospace, the radiation belts and the ionosphere, can become strongly disturbed. These storms increase fluxes of energetic electrons that can permanently damage satellite electronics, disrupting telecommunications and GPS technologies, and can also be a hazard to astronauts, even in low Earth orbit. They also create aurorae seen near the magnetic poles.
Although it meets the definition of outer space, the atmospheric density within the first few hundred kilometers above the Kármán line is still sufficient to produce significant drag on satellites. This region contains material left over from previous manned and unmanned launches that are a potential hazard to spacecraft. Some of this debris re-enters Earth's atmosphere periodically.
Cislunar space
The region outside Earth's atmosphere and extending out to just beyond the Moon’s orbit, including the Lagrangian points, is sometimes referred to as cis-lunar space.Interplanetary space
 |
The sparse plasma (blue) and dust (white) in the tail of comet Hale–Bopp are being shaped by pressure from solar radiation and the solar wind, respectively |
The volume of interplanetary space is a nearly total vacuum, with a mean free path of about one astronomical unit at the orbital distance of the Earth. However, this space is not completely empty, and is sparsely filled with cosmic rays, which include ionized atomic nuclei and various subatomic particles. There is also gas, plasma and dust, small meteors, and several dozen types of organic molecules discovered to date by microwave spectroscopy. A cloud of interplanetary dust is visible at night as a faint band called the zodiacal light.
Interplanetary space contains the magnetic field generated by the Sun. There are also magnetospheres generated by planets such as Jupiter, Saturn, Mercury and the Earth that have their own magnetic fields. These are shaped by the influence of the solar wind into the approximation of a teardrop shape, with the long tail extending outward behind the planet. These magnetic fields can trap particles from the solar wind and other sources, creating belts of magnetic particles such as the Van Allen radiation belt. Planets without magnetic fields, such as Mars, have their atmospheres gradually eroded by the solar wind.


